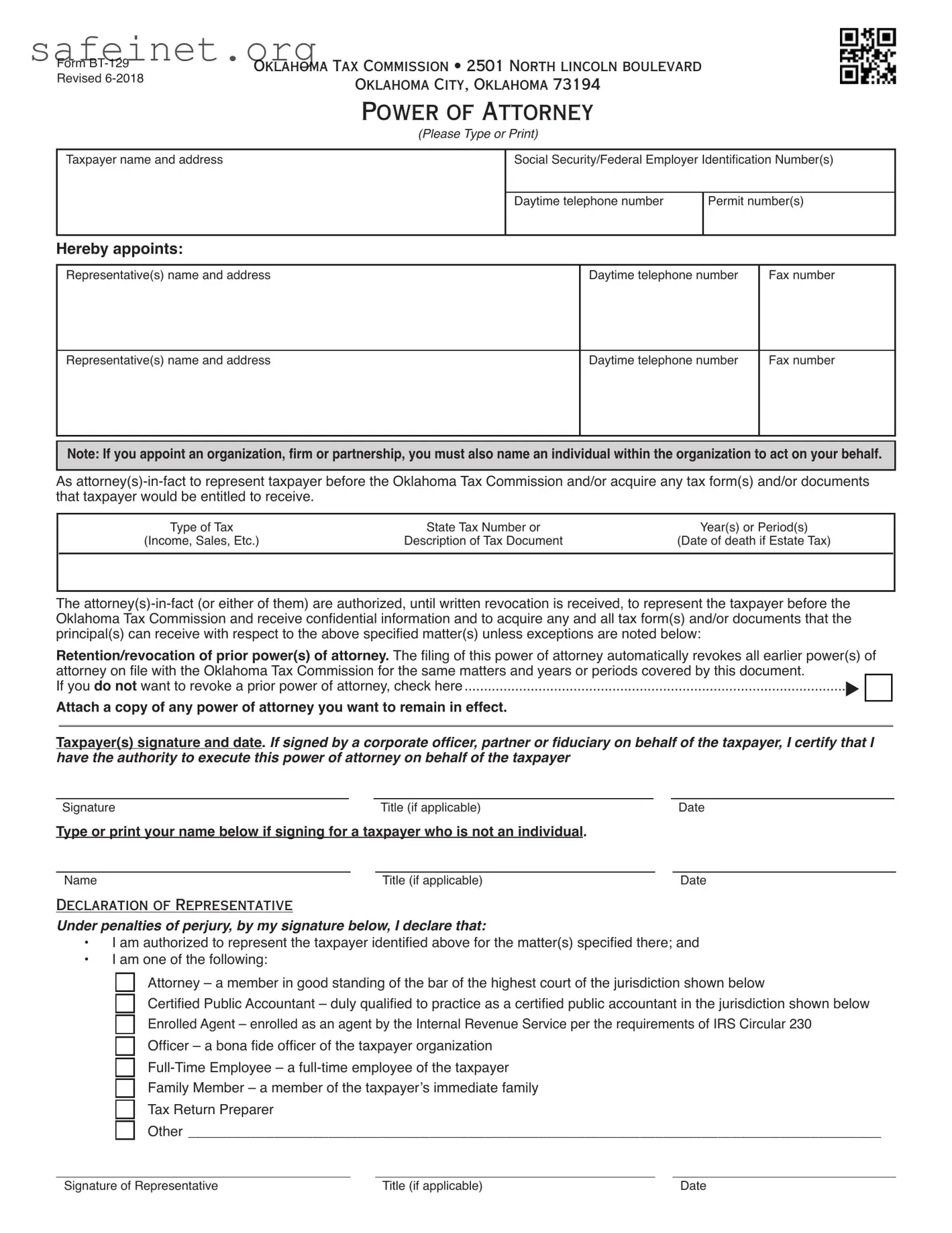
What is the Tax POA form BT-129?
The Tax POA form BT-129 is a document that allows individuals to designate a representative to act on their behalf regarding tax matters. This form is commonly used by taxpayers who need assistance from a tax professional or attorney when dealing with tax authorities.
Who should use the BT-129 form?
This form is ideal for anyone who requires help with their tax filings or disputes. Whether you're an individual taxpayer facing a complicated issue, or a business owner needing support while navigating tax regulations, the BT-129 form can facilitate communication with tax agencies.
How do I complete the BT-129 form?
To complete the BT-129 form, you'll need to provide the taxpayer's information, including their name, address, and tax identification number. Additionally, you'll list the representative's details, including their name, contact information, and any specific tax matters they are authorized to handle. Be sure to sign and date the form before submitting it.
Do I need to file the BT-129 form with my tax return?
No, the BT-129 form is a separate document and does not need to be filed with your tax return. Instead, submit the form directly to the relevant tax authority. This allows your representative to interact with the agency without needing to be present at all times.
How long does it take for the BT-129 form to be processed?
The processing time for the BT-129 can vary based on the tax agency’s workload. Typically, it may take anywhere from a few weeks to a couple of months for your form to be processed. After submission, keep an eye out for any confirmations or follow-up requests from the tax authority.
Can I revoke the POA granted by the BT-129 form?
Yes, you can revoke the Power of Attorney at any time. To do this, completing a revocation form or writing a formal letter indicating your desire to cancel the POA will suffice. Be sure to notify your representative and the relevant tax authority to ensure the revocation is recognized.
Is there a fee associated with the BT-129 form?
There is no fee for filing the BT-129 form itself. However, if you choose to hire a tax professional or attorney to assist you, they may charge fees for their services. Make sure to clarify any potential costs before agreeing to their assistance.
Can more than one person be listed as a representative on the BT-129 form?
Yes, you can designate multiple representatives on the BT-129 form. List each representative's information clearly and make sure their roles and responsibilities are defined. This can be helpful if you want different professionals handling various aspects of your tax matters.
What if my representative doesn’t act in my best interest?
If you believe your representative is not acting in your best interest, you can revoke the POA at any time. After revocation, you should consider finding another representative or managing your tax matters independently. Protecting your interests is paramount.
How can I ensure my information remains confidential when using the BT-129 form?
When filling out the BT-129 form, ensure that you provide it only to authorized individuals or tax authorities. Use secure means to transmit the form, and remind your representative of their obligation to keep your information confidential. Being vigilant about your data protection is essential in tax matters.