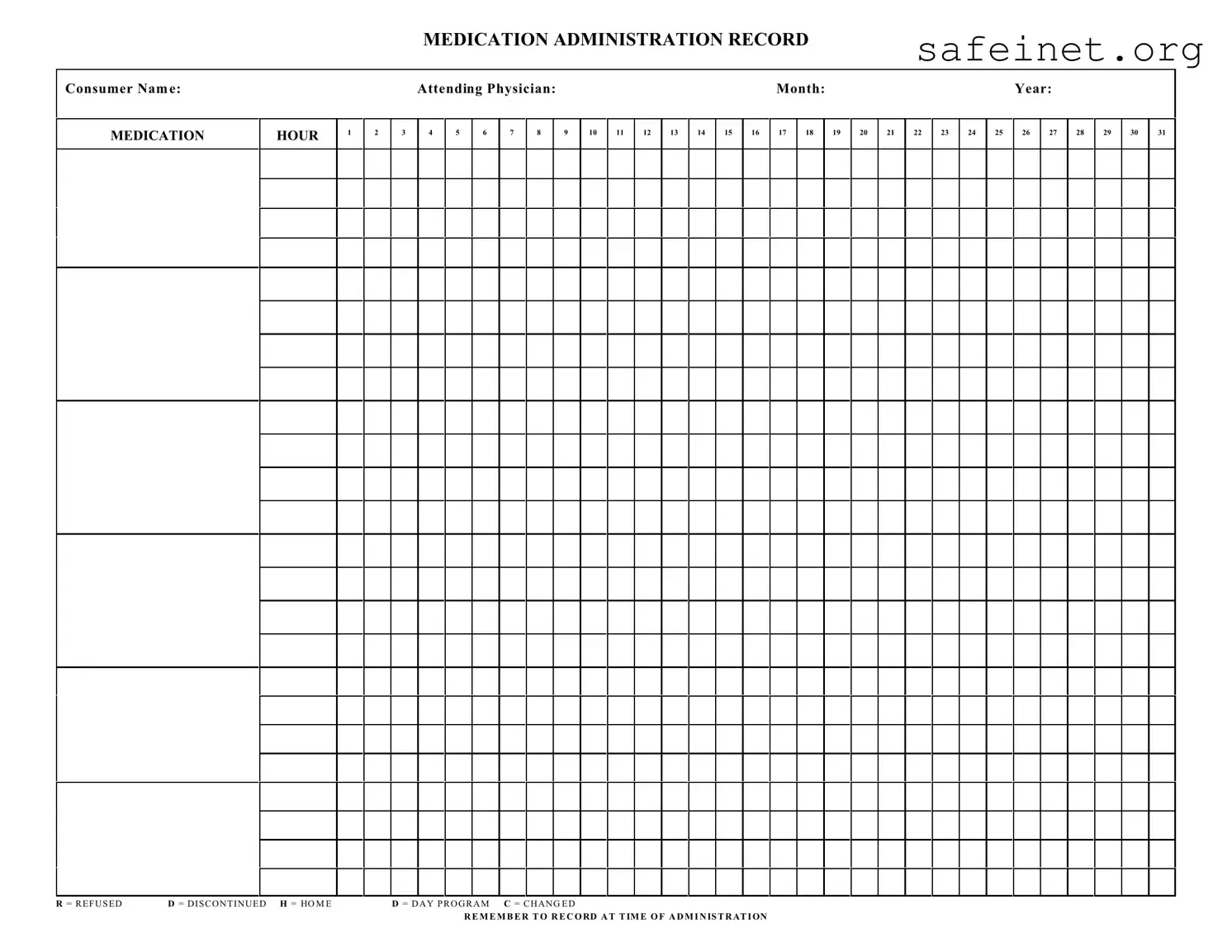
What is a Medication Administration Record Sheet (MARS)?
A Medication Administration Record Sheet is a vital tool for tracking medication administered to a consumer. This form records various details, including the consumer's name, attending physician, and the specific month and year. It ensures that medication is given at the correct times while offering a clear record in case of inquiries or audits.
How do I use the Medication Administration Record Sheet?
To utilize the MARS, start by filling in the consumer's name, attending physician, and the date (month and year). When administering medication, note the hour in the corresponding box. If a medication is refused or discontinued, mark it as instructed: 'R' for refused and 'D' for discontinued. Remember to record all actions at the time of administration for accuracy.
What should I do if a medication is changed?
If a medication has been changed, indicate this on the MARS by marking 'C' in the box corresponding to the medication time. Ensure all staff members are aware of the change to avoid administration errors. It's crucial to follow up by updating any relevant documents regarding the consumer's medication regimen.
Why is it important to record medication administration accurately?
Accurate records are essential for multiple reasons. First, they help ensure consumer safety by preventing medication errors. Second, they provide essential documentation for healthcare providers to review the consumer's treatment history. In addition, proper recording can help comply with regulatory requirements to demonstrate accountability and transparency in medication management.