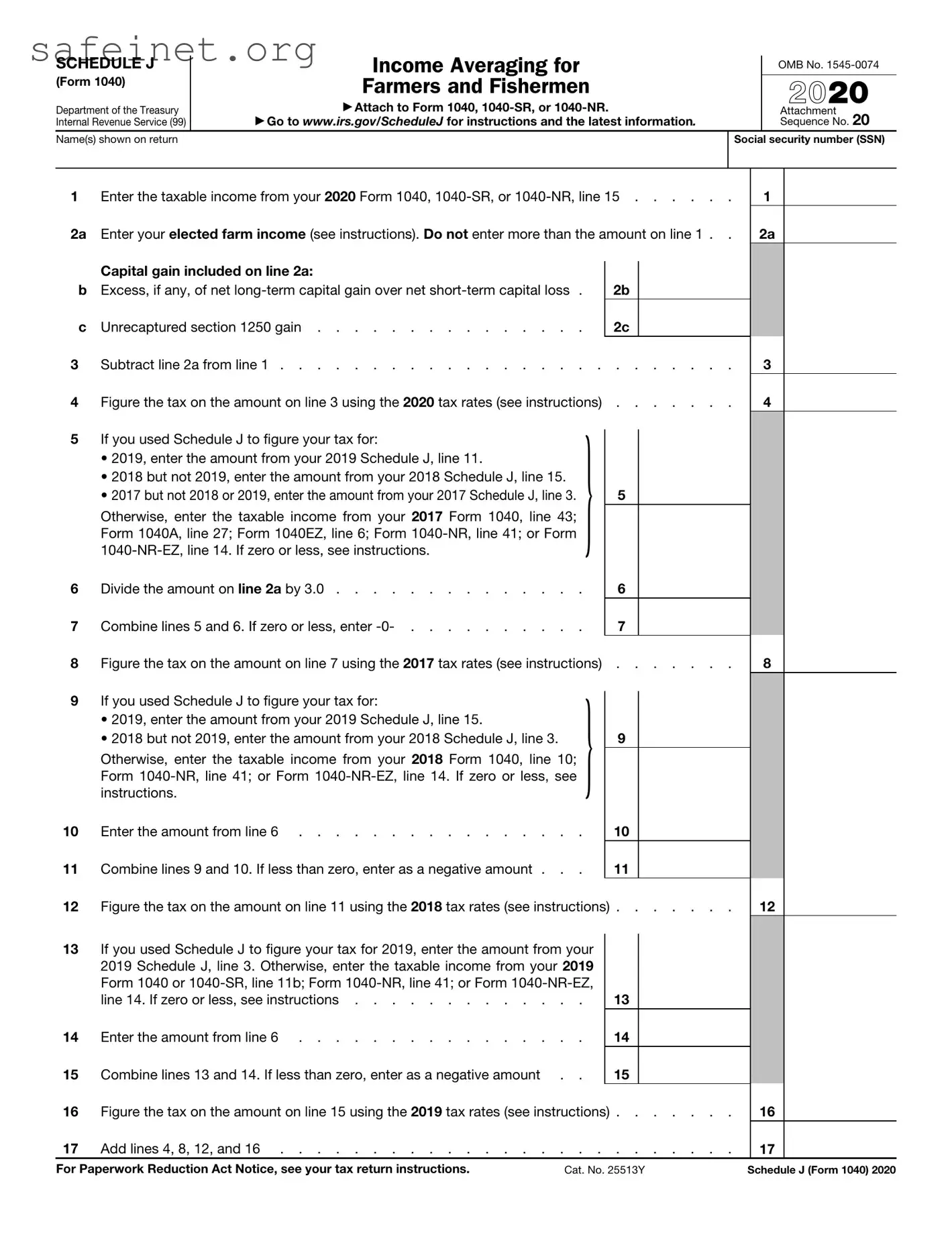
What is IRS Schedule J?
IRS Schedule J is a form used by farmers and fishermen to calculate their average annual income over a period of three years. By using this form, individuals can smooth out fluctuations in their income, making it easier to handle taxes and plan for future financial stability. This is especially beneficial for those whose income varies significantly from year to year due to seasonal factors or unpredictable market conditions.
Who needs to file Schedule J?
Farmers and fishermen who report their income on Schedule F (Profit or Loss from Farming) or Schedule C (Profit or Loss from Business) must consider filing Schedule J. If their gross income exceeds a certain threshold or if they want to take advantage of income averaging, completing this form may be necessary. Additionally, taxpayers who have a substantial decline in their income may also find this option advantageous.
How do I complete Schedule J?
To fill out Schedule J, begin by gathering your income data for the current year and the two preceding years. Calculate the total income for all three years and then find the average by dividing this figure by three. Fill in the required personal information at the top and report your average income on the designated lines. It's crucial to follow the steps carefully, as any miscalculations can lead to issues with your tax return.
Can I use Schedule J with other tax forms?
Yes, Schedule J can be used in conjunction with your IRS Form 1040 and other forms such as Schedule F or Schedule C. However, it is important to ensure that the averages calculated on Schedule J align with the figures reported on additional forms. This helps maintain consistency throughout your tax return and can reduce the likelihood of errors or inquiries from the IRS.
What are the benefits of using Schedule J?
Utilizing Schedule J allows farmers and fishermen to level out their income for tax purposes. This averaging can lead to lower tax liability in years where income spikes. Furthermore, it can prevent larger tax bills during profitable years, easing the financial burden. By applying this method, individuals may experience better cash flow throughout the year, allowing for more strategic financial planning.
Are there specific deadlines for filing Schedule J?
Schedule J must be filed alongside your Form 1040, adhering to the standard deadlines for individual tax returns. Generally, this means that tax returns are due on April 15. However, if you qualify for an extension, you can file later, although payments are still due by the original deadline to avoid penalties and interest.
What if I make a mistake on Schedule J?
If you discover an error after filing, you can correct it by submitting an amended tax return using Form 1040-X. It’s important to act promptly and provide accurate information about the changes made on Schedule J. This helps maintain compliance with tax regulations and minimizes the risk of penalties.