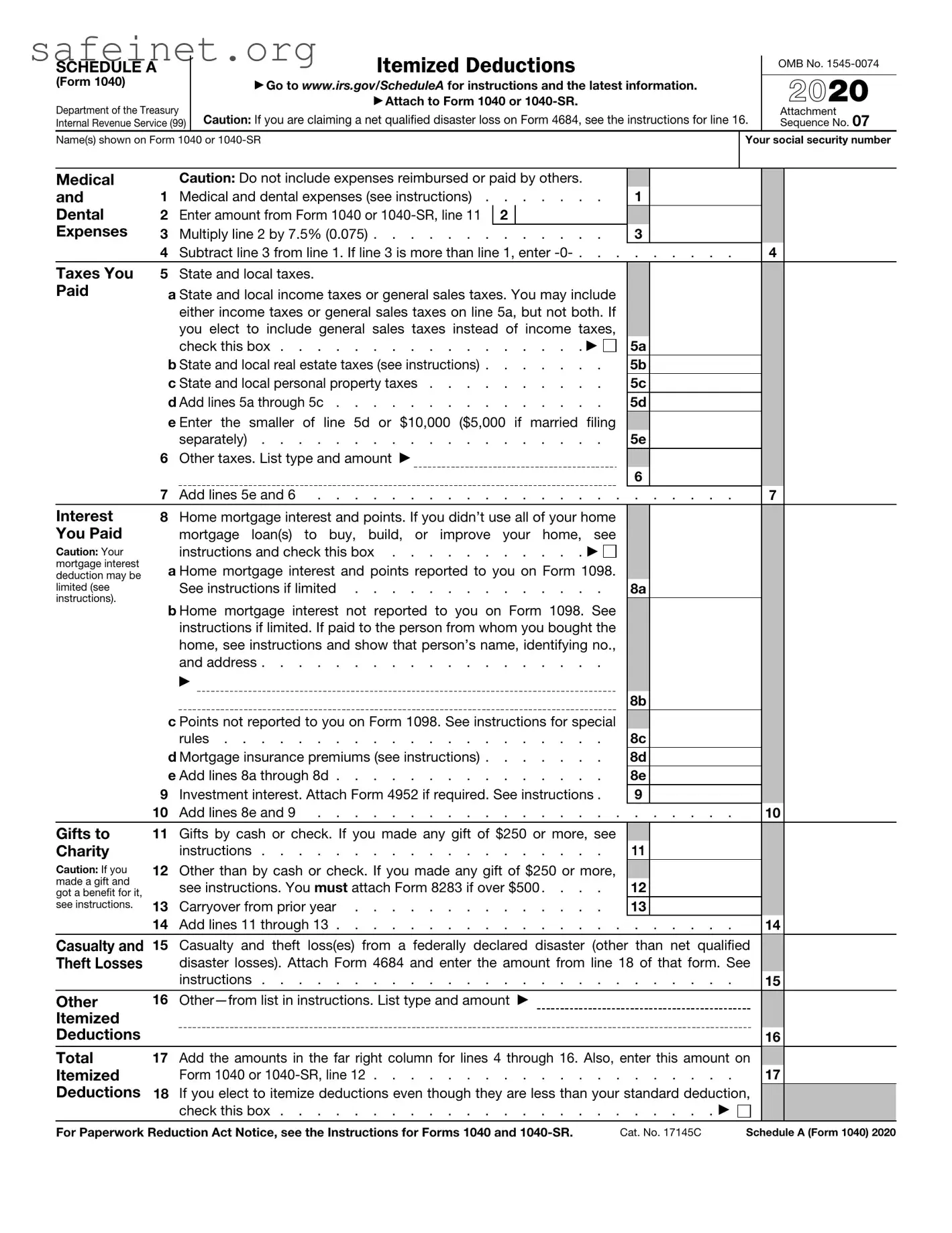
The IRS Form 1040 is akin to the tax returns required by other countries, which similarly offer a way for individuals to report their income, deductions, and taxes owed. Just as the 1040 form develops a comprehensive view of an individual’s financial situation in the United States, forms in other countries tailor specific schedules to their tax systems. They often require detailed disclosures about income sources and applicable deductions, reflecting local tax laws and regulations. Like the 1040, these forms aim to ensure accurate reporting while determining a taxpayer’s liabilities or refunds.
The IRS Form W-2 provides a detailed account of an employee's earnings and tax withholdings for the year. It serves as a companion to the Form 1040, as taxpayers use the information from W-2s to fill in their income section. In this way, the W-2 acts as a crucial building block within the tax filing process. This document not only lists wages but also specifies taxes withheld by the employer, which is vital for accurately calculating final tax obligations on the 1040 form.
Another document closely related to the IRS Schedule A is Form 1098, which reports mortgage interest and tuition payments. Individuals claiming deductions for home mortgage interest or educational expenses can use the information on Form 1098 to substantiate their claims on Schedule A. This similarity underscores the importance of documenting expenses to reduce taxable income, ensuring taxpayers benefit from potential deductions while adhering to IRS regulations.
Form 1099 is also similar to Schedule A, especially for reporting various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. Various categories of 1099 forms report freelance earnings, investment income, and dividends. Taxpayers use this information to accurately report total income on the 1040 form. Thus, Form 1099 contributes to a complete income picture for individuals aiming to diminish potential tax liabilities.
Form Schedule C is used by sole proprietors to report income or loss from their business, sharing similarities with Schedule A since both formats detail specific financial activities. While Schedule A focuses on itemized deductions, Schedule C emphasizes profits and expenses from self-employment. Both documents help taxpayers illustrate their financial situations to the IRS and demonstrate their efforts to comply with federal tax obligations.
The IRS Form 8889 is relevant for individuals with Health Savings Accounts and parallels the Schedule A form when addressing medical expense deductions. Taxpayers can report contributions to HSAs and the subsequent tax advantages linked to those contributions. This form enhances Schedule A as it provides another layer of deduction related to healthcare, allowing individuals to maximize their potential tax benefits.
Form 8862 works in conjunction with the IRS Schedule A for people who have previously claimed the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) but need to revalidate their eligibility. In cases of disallowance, this form helps rectifying past mistakes. Taxpayers can utilize it to demonstrate compliance with reporting requirements, ensuring their right to claim specific tax credits on their 1040 forms.
Schedule B, which details interest and dividend income, aligns with Schedule A by revealing additional sources of income subject to taxation. Taxpayers who itemize deductions commonly benefit from a clearer understanding of total financial inflows and outflows. Including Schedule B information reinforces a comprehensive approach to income reporting on the 1040, thereby aiding in determining tax obligations accurately.
Form 8863 is associated with education credits and bears similarities to Schedule A since both forms can reduce taxes owed. While Schedule A itemizes deductions, Form 8863 covers credits related to educational expenses. Both require taxpayers to provide documentation and calculation details related to financial outlays, enhancing their overall tax filing strategy and minimizing liability.
Lastly, the IRS Form 4506-T allows taxpayers to request a transcript of their previous tax returns, which may serve to support deductions claimed on Schedule A. By providing insights into prior filings, this form aids individuals in ensuring consistency in their tax reporting. Accessing historical data through Form 4506-T becomes particularly useful if additional verification of past deductions or income sources is needed.