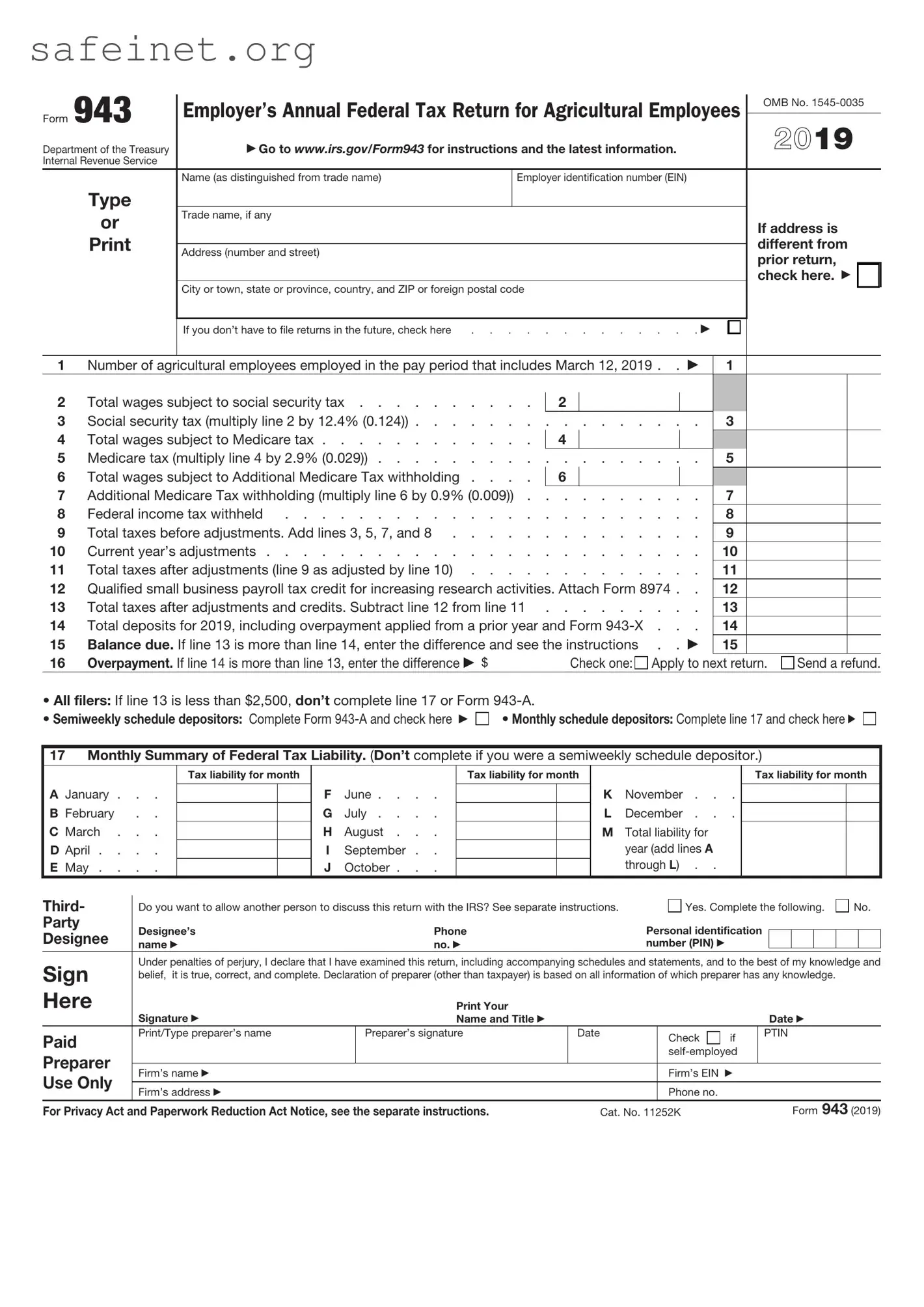
The IRS 941 form is a quarterly tax return used by employers to report income taxes withheld from employees' paychecks, along with Medicare and Social Security taxes. This form, like IRS 943, is important for ensuring compliance with tax regulations. While IRS 943 is specifically for agricultural employers reporting annual taxes, IRS 941 caters to a broader range of employers and is submitted more frequently throughout the year.
The IRS W-2 form summarizes an employee's annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld. Employers use this document to provide employees with a comprehensive overview of their earnings and taxes for the year. Similar to the IRS 943, the W-2 is essential for tax filing, but it focuses on individual employee information rather than the tax liabilities of the employer.
The IRS W-3 form is a transmittal form that accompanies the W-2 filings. It aggregates the total earnings and tax withheld for all employees. Like IRS 943, which aggregates annual tax information for agricultural employers, the W-3 provides a summary to the IRS, ensuring accurate reporting of total wages and tax contributions.
The IRS 1099 form is used to report various types of income other than wages, salaries, or tips. This form is crucial for independent contractors and other non-employees. While IRS 943 applies to employers in the agriculture sector and focuses on employment taxes, the 1099 series serves a different purpose in reporting payments made to individuals who are not classified as employees.
The IRS 940 form serves as an annual report for federal unemployment taxes. Similar to IRS 943, which addresses specific taxes related to agricultural payroll, the 940 form helps employers report their contributions towards federal unemployment insurance. Both forms are pivotal for compliance with federal tax regulations, albeit for different funding purposes.
The IRS Schedule H is an attachment for filers who employ household employees and need to report taxes on their wages. While both Schedule H and IRS 943 involve reporting employment taxes, Schedule H is targeted towards domestic staff, while 943 caters to agricultural workers, highlighting the different employment contexts addressed by these documents.
The IRS 1065 form is filed by partnerships to report income, deductions, and credits. This form does not focus primarily on employment taxes like IRS 943 but is important for tax compliance among partnerships. Both forms share the objective of ensuring accurate reporting to the IRS, but they cover different types of business structures and tax obligations.
The IRS 1120 form is utilized by corporations to report their income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits. Like IRS 943, it is essential for tax compliance; however, the 1120 form pertains to corporate entities rather than agricultural employers. Both documents play a vital role in the broader context of tax reporting and obligation fulfillment.
The IRS Form 5558 is used to apply for an extension of time to file certain employee benefit plan returns. This form is similar to IRS 943 in that both involve deadlines and filings concerning certain fiscal responsibilities. However, Form 5558 specifically addresses retirement and employee benefit plans, while IRS 943 is focused on agricultural employment taxes.