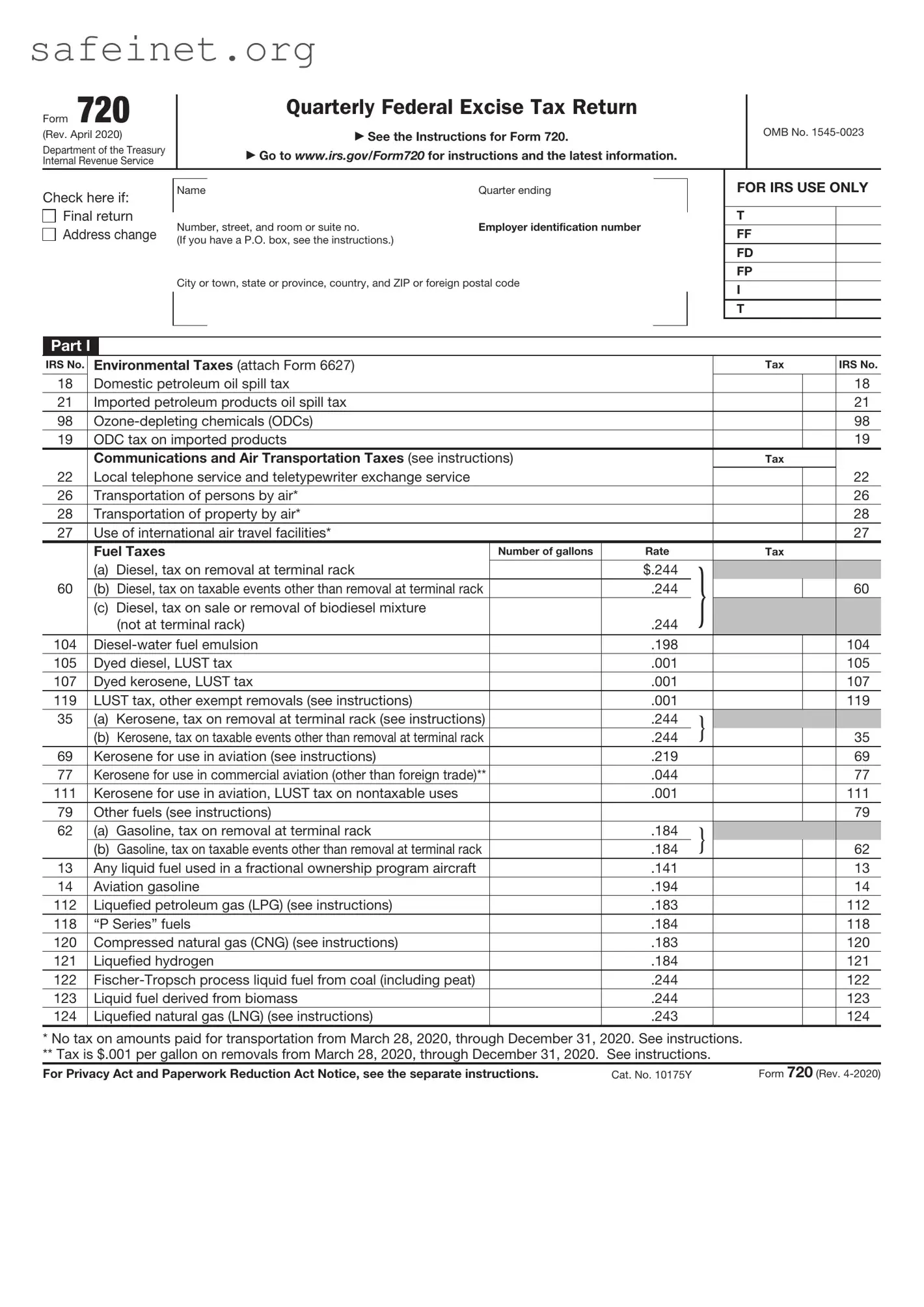
What is the IRS Form 720?
The IRS Form 720 is a tax form used to report and pay federal excise taxes. This includes taxes on specific goods, services, and activities. Businesses or individuals who engage in these activities may be required to use this form to report any applicable excise taxes owed to the IRS.
Who needs to file Form 720?
Any business or individual that owes federal excise taxes must file Form 720. This could include manufacturers, importers, and distributors of certain goods, as well as service providers in areas such as communications or environmental impact. If you're unsure, it’s wise to consult a tax professional.
When is Form 720 due?
Form 720 is typically due quarterly. The deadlines for each quarter are as follows: April 30 for the first quarter, July 31 for the second, October 31 for the third, and January 31 of the following year for the fourth. Timely filing helps avoid penalties and interest.
What types of taxes are reported on Form 720?
Form 720 covers a variety of excise taxes. These include fuel taxes, taxes on air transportation, and environmental taxes, among others. It's essential to review which specific taxes your business is liable for and report them accordingly.
How do I complete Form 720?
Start by gathering the necessary information about your business and the applicable excise taxes. Next, fill out the form, providing all required details and calculations. Make sure to check for accuracy before submission. Detailed instructions are available on the IRS website to assist you.
Can I file Form 720 electronically?
Yes, you can file Form 720 electronically through the IRS e-file system. Electronic filing can be more efficient and offers the benefit of quicker processing and confirmation of receipt. Many tax software programs simplify this process for you.
What if I don’t file Form 720 on time?
If you miss the deadline, you may face penalties and interest on any unpaid taxes. The IRS typically calculates the penalty based on the amount owed and the duration of the delay. It's important to file as soon as possible to minimize these consequences.
Can I correct a mistake on Form 720 after filing?
Absolutely. If you realize that you’ve made a mistake after submitting Form 720, you can file an amended return. Use the IRS Form 720-X to correct any errors. Be sure to include detailed information about what needs to be changed to avoid issues.
Where do I send my completed Form 720?
Where you send your completed Form 720 depends on your location and whether you're including a payment. Specific mailing addresses are available on the IRS website. It's crucial to check these details to ensure timely processing of your form.
How can I get more help with Form 720?
If you need more assistance, the IRS provides resources online, including instructions for completing Form 720. Additionally, you can contact the IRS directly or consult a tax professional for personalized guidance. Don't hesitate to reach out for help if you need it!

 Final return
Final return