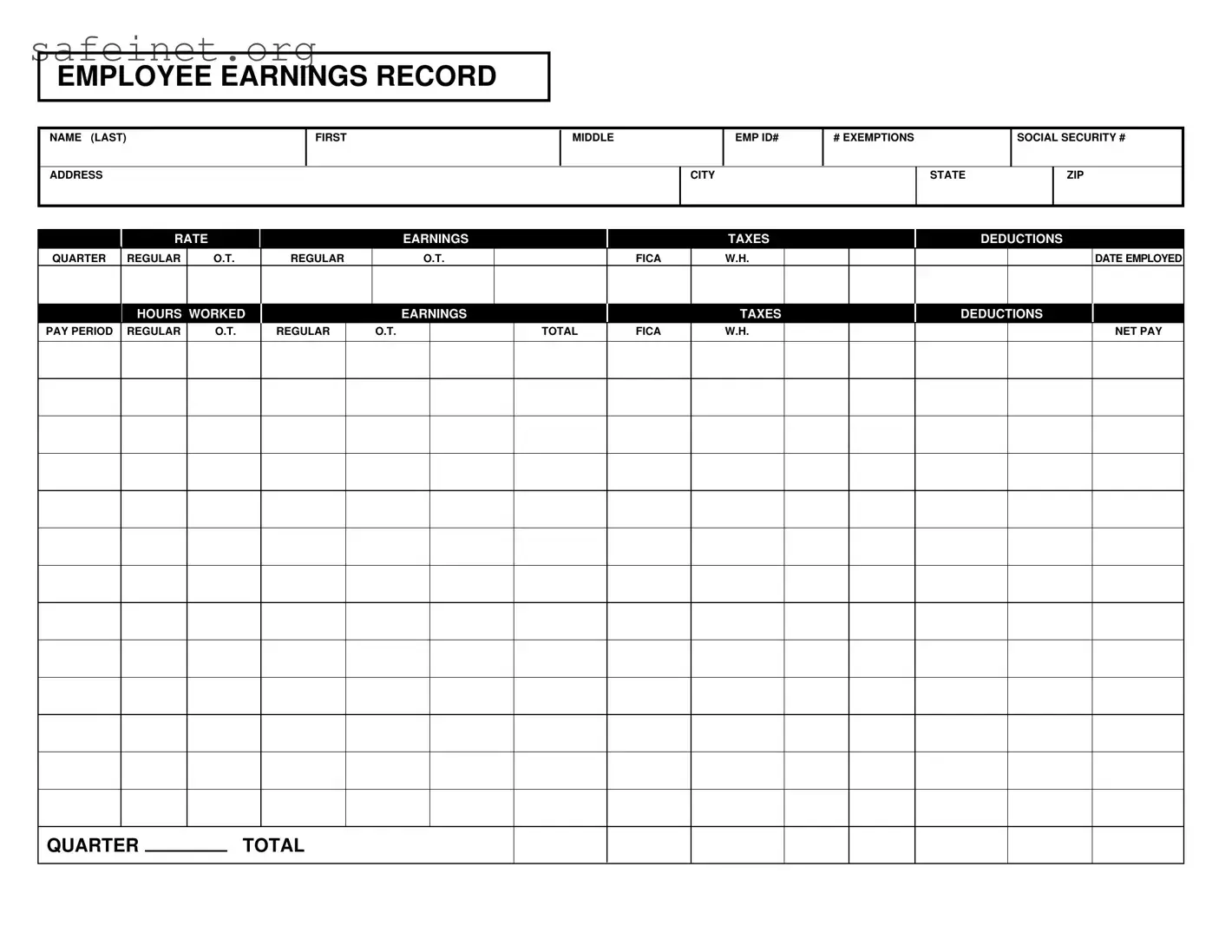
What is the Employee Earnings Record form?
The Employee Earnings Record form is a crucial document for tracking an employee's earnings, taxes, and deductions throughout their employment. It includes information such as the employee’s name, address, social security number, and employment ID, as well as details regarding their earnings over different pay periods, including both regular and overtime hours worked.
Why is the Employee Earnings Record important?
This form is essential because it provides a comprehensive summary of an employee's financial history within the company. It serves as a reference for calculating taxes and benefits, preparing end-of-year tax documents, and managing payroll effectively. Accurate records are critical for compliance with federal and state regulations.
What information is required on the Employee Earnings Record?
The form requires several key pieces of information, including the employee's name (first, middle, last), address, social security number, employment ID, tax exemptions, and details about their earnings. It also requires information on hours worked, earnings (both regular and overtime), applicable taxes, deductions, and net pay for each pay period.
How often should the Employee Earnings Record be updated?
The Employee Earnings Record should be updated regularly, ideally after each pay period. This ensures that all data remains current and accurate. Regular updates help prevent any discrepancies during tax preparation or while addressing employee inquiries regarding their pay.
Who is responsible for maintaining the Employee Earnings Record?
The payroll department typically handles the maintenance of the Employee Earnings Record. However, it’s important for employees to also review their records periodically to verify accuracy. If any errors are found, employees should report them promptly to the appropriate department.
What is the difference between regular and overtime earnings on the form?
Regular earnings refer to the standard pay an employee receives for their regular hours of work. Overtime earnings are compensation for hours worked beyond the typical 40-hour workweek, which is usually paid at a higher rate. Both types of earnings are documented separately on the Employee Earnings Record to ensure accurate calculations for wages and taxes.
How do taxes and deductions appear on the Employee Earnings Record?
Taxes and deductions are itemized on the Employee Earnings Record to provide clear visibility on how much was withheld from the employee's earnings. This includes federal income tax (W.H.), FICA taxes, and other deductions that may pertain to benefits or retirement contributions. This transparency helps employees understand their net pay calculations.
When can an employee request a copy of their Employee Earnings Record?
Employees are typically entitled to request a copy of their Employee Earnings Record at any time. They may do so for personal recordkeeping, tax preparation, or to verify employment earnings. Employers should have a procedure in place to fulfill these requests promptly and efficiently.