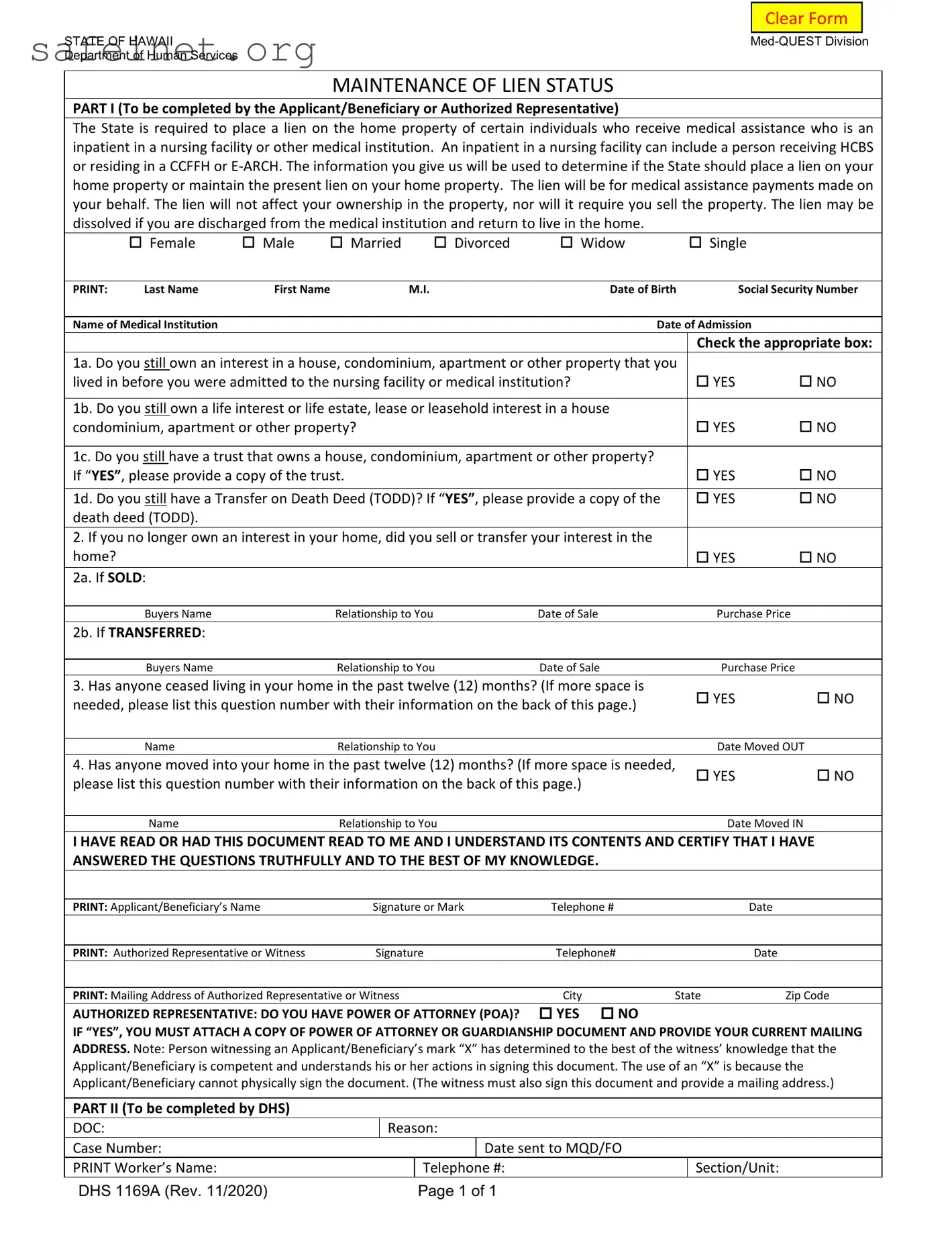
The DHS 1169 form is quite similar to the Medicaid Application form. Both documents serve to gather essential information regarding an individual's assets and financial status. The Medicaid Application focuses on determining eligibility for the program, while the DHS 1169 form centers around assessing whether a lien should be placed on an applicant’s property for medical assistance received. Both forms require information about the applicant's income, assets, and living arrangements, ensuring that the applicant complies with state regulations.
Another comparable document is the Notice of Lien form. This form, like the DHS 1169, deals with liens on property but primarily serves to inform individuals that a lien has been placed against their property due to unpaid debts or obligations. Both forms require specific information about the property and the individual, establishing a formal record of the state's interest in the property. While the Notice of Lien focuses on enforcement of debts, the DHS 1169 assesses the need for a lien related to healthcare costs.
The Durable Power of Attorney document is also related, as it often accompanies forms like the DHS 1169 when an authorized representative is involved. This document allows one person to make decisions on behalf of another, particularly in matters relating to health care and finances. The DHS 1169 form potentially requires a power of attorney to be attached when a representative completes the application, ensuring the representative acts within their legal rights to manage the applicant’s affairs.
The Arizona Long Term Care application shares similarities with the DHS 1169 form as both focus on securing benefits for long-term care expenses. Individuals are required to provide personal and financial details to determine the need for a lien in relation to their assets. Both applications assess home ownership and any associated liens that might be required to manage costs incurred during extended medical care.
Your resources also overlap with the Elderly Waiver Application. This form provides assistance to eligible elderly individuals, ensuring they receive necessary medical attention while keeping home property intact. Similar to the DHS 1169, the Elderly Waiver Application also reviews property ownership and establishes criteria for what circumstances may lead to a lien on an individual's home.
The Supplemental Security Income (SSI) application is relevant to the DHS 1169 form as well. Both documents assess financial need to qualify for assistance programs. While SSI provides monthly cash benefits based on financial limitations, the DHS 1169 focuses specifically on determining lien conditions tied to medical assistance, often involving similar income and asset assessments.
The Estate Recovery Program form is another document related to the DHS 1169. This state program can seek reimbursement from the estate of a deceased beneficiary for certain Medicaid expenses. While the DHS 1169 assesses current lien status on properties belonging to living individuals, both documents ultimately deal with the state’s recovery rights regarding medical costs, emphasizing the importance of property ownership in the context of financial assistance.
Similarly, the Long-Term Care Insurance policy document shares notable characteristics with the DHS 1169 form. Both documents require applicants or their representatives to disclose information concerning ownership of property and assets. Whereas the Long-Term Care Insurance policy aims to provide an alternative means to cover care costs, the DHS 1169 evaluates the necessity of placing a lien on a property for medical assistance received, helping to safeguard the interests of both the beneficiary and the state.
The Medicare Secondary Payer form also bears resemblance to the DHS 1169 because both handle issues pertaining to healthcare coverage and the complex coordination of benefits. Medicare involves determining which insurance will pay first in cases of overlapping eligibility, while the DHS 1169 centers on assessing whether a lien is necessary for medical assistance, facilitating the management of healthcare costs effectively.
Finally, the Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS) application pertains to individuals needing assistance while remaining in their homes. Like the DHS 1169, it explores living arrangements and assets. Both forms aim to protect the interests of individuals receiving health services, ensuring that assistance does not require liquidating or losing their homes to cover medical expenses.