What is the purpose of the CMS 802 form?
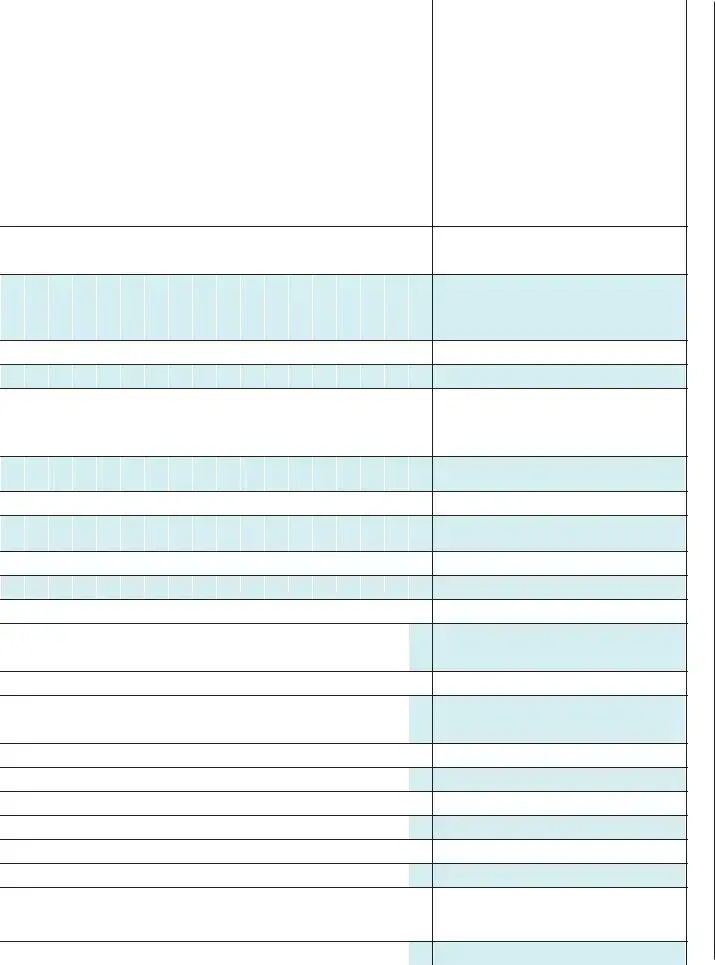
The CMS 802 form, also known as the Matrix, is used to document specific care categories for residents in a healthcare facility. It identifies residents admitted within the last 30 days and helps assess various health conditions and care needs, ensuring that all pertinent information is available for quality care management.
Who is responsible for completing the CMS 802 form?
Staff members who are knowledgeable about the resident population should complete the form. This ensures that the information entered is accurate and reflects the current status of all residents as of the day of the survey.
What information is required when filling out the CMS 802 form?
When completing the CMS 802 form, providers must include the resident's name, room number, and mark relevant columns from 1 to 20 that pertain to the resident's care categories. Each resident will require individual attention to accurately reflect their health conditions and medications.
What types of health conditions does the CMS 802 form cover?
The CMS 802 form covers a wide range of health conditions. These include Alzheimer's or dementia, pressure ulcers, excessive weight loss, tube feeding needs, falls, urinary catheter use, dialysis, and various infections, among others. Each category provides critical information for overseeing resident care.
How should medications be recorded on the CMS 802 form?
Medications should be recorded based on their pharmacological classification rather than their intended use. For example, medications like insulin, anticoagulants, antibiotics, and opioids should be noted accordingly. This categorization helps in understanding the types of medications each resident requires.
What does it mean if a resident has a “facility acquired” pressure ulcer?
A pressure ulcer is considered "facility acquired" if it developed after the resident's admission to the facility. This notation is important for quality assurance and helps in evaluating the facility's ability to prevent such conditions.
Are there any exclusions for residents specifically noted on the CMS 802 form?
Yes, certain criteria apply. For instance, residents receiving hospice services are excluded from the excessive weight loss column. This exclusion ensures that the focus remains on those who are not in end-of-life care when assessing weight changes.
When should the CMS 802 form be filled out?
The CMS 802 form should be filled out to reflect the current status of residents as of the date of the survey. It is crucial that all marking occurs only after a thorough review by informed staff members to ensure accuracy.



















 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21